Requirements
Operating system
We do not support or test end-of-life distribution versions. For example, no Debian 9. You should aim to stay in the range of distribution versions that are supported by the distribution vendor, e.g. Ubuntu 18.04 at the start of 2024. With Red Hat, we started our support with version RHEL 8.1.
Linux kernels before 3.17 are too old.
Also follow the requirements of your container engine (Docker or podman).
As we only provide linux container images, you need a Linux operating system or a Linux virtual machine.
Level of integration and support:
| operating system | integration | obtainable support by Programmfabrik GmbH |
|---|---|---|
| Debian 11, 12 | production ready, tested | installation and maintenance |
| Ubuntu 20.04, 22.04 | production ready, tested | installation and maintenance |
| RedHat Enterprise Linux RHEL 8.1 | production ready via podman, tested | installation and maintenance |
| RedHat Enterprise Linux RHEL other versions | testing possible but no integation done | answers about some aspects |
| SLES | testing possible but no integation done | none |
| MacOS | no native integration possible | none |
| Windows Server 2019 | no native integration possible but experimental grafting via virtual machine done, testing possible | answers about some aspects |
If you want Programmfabrik to fullfill a maintenance contract on a server then only via ssh access, for a 64 bit version, for which there are recent security updates.
We have not measured the amount of performance degradation by the additional virtualization for Windows or MacOS. We do not recommend those platforms and do not support them.
Are you interested in directly downloading a recommended operating system?
- Go to http://cdimage.debian.org/debian-cd/current/amd64/iso-cd
- Download the file that starts with
debian-1and ends with-amd64-netinst.iso.
Software under Debian and Ubuntu
Docker up to (at least) Version 20 prevents the start of newer versions of our elasticsearch container.
Versions from 24.0.7 on are new enough, and probably a few versions below that as well.
The Community Edition (CE) is quite sufficient. We recommend the “stable” channel and assume the default architecture x86_64.
If we are installing the easydb for you then we will also install Docker ourselves. But please make sure that the requirements for Docker are met.
Here is a link to the installation guide for Docker under e.g. Debian.
Software under Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.1
podman (docker replacement)
For details, e.g. the dnsname plugin for podman, see our installation guide.
Hardware
CPU & RAM
4 processor cores,
- plus 1 core for each
250000records (Recommendation. Depending on your usage, more.)
16 GB of RAM,
- plus 4GB RAM for each
250000records (Recommendation. Depending on your usage, more.)
Example calculation:
easydb5 has 1234567 Records
So you have to calculate the following:
CPU: 1234567 / 250000 = 4,9 --> 5
RAM: 1234567 / 250000 = 4,9 --> 5
CPU: 5 + 4 = 9 Cores
RAM: 5*4 + 16 = 36 GB RAM
Please keep in mind that this is only a guideline and the number of resources needed depends on many factors.
Docker may have further requirements, e.g. 64 bit processor cores. These are mentioned in the Docker installation guide.
Storage
Storage space:
- Summary: 140 GB plus 205% of the spaced used by your assets.
- Example: If you got 1000 GB of assets, you need 140+2050=2190 GB storage space.
- In the following points we will explain this in detail. Also see Filesystem Layout further below.
- 60 GB for the container files of the easydb. These grow slowly over time, starting from about 8 GB.
- 50 GB for temporary files, such as intermediate conversion results or files for the zoom function.
- 30 GB for the operating system and log messages.
- 200% of the storage space of the assets which you want to manage with easydb. 100% is your assets and another 100% for preview versions. If you need additional large preview versions, you also need more storage. Assets and preview versions can be stored on network storage (more on network storage below). These and database dumps are the only types of data which can be on network storage.
- 4% additional storage space for databases. The databases are the first to put on fast storage (e.g. SSDs). But this is optional.
- 1% additional storage space for database-dumps.
- We recommend to not have /boot as a separate partition but instead as part of the root partition. If you do separate it, we recommend at least 1 GB in /boot to accommodate the accumulating kernel versions.
- Here are two examples from production environments (“Small” and “Large”):
| Storage Requirements | Assets | Preview Versions | SQL DB | Elasticsearch DB |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small example | 60 GB | 20 GB | 1,5 GB | 0,07 GB |
| Large example | 15,000 GB | 15,000 GB | 224 GB | 180 GB |
| Rule of thumb | 100% of assets | 100% of assets | 2% of assets | 2% of assets |
| (… continued) | easydb software (docker) | SQL dumps | temporary files |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small example | 18 GB | 0,3 GB | 0 GB |
| Large example | 54 GB | 53 GB | 32 GB |
| Rule of thumb | 60 GB | 1% of assets | 50 GB |
Network Storage
If you use network storage then we recommend the NFS protocol. CIFS can also work, but we have seen performance problems on some Windows servers without remedy and even data corruption - thus we do not support CIFS/SMB. Also NFS on a Windows server has been observed to have poor performance compared to Linux servers.
At most, put assets, previews and database dumps on network storage.
Inodes are not a limiting factor when defaults of Linux file systems are used. However if your network storage enforces an inode quota, then make sure to provide at least 30 inodes per asset (on the file system storing the assets and previews).
Filesystem Layout
Assumptions: 1000 GB assets, base directory (“data store”) is /srv/easydb
Example “separated by storage type without getting too much into details”:
| storage space | directory | candidate for … |
|---|---|---|
| 90 GB | / | |
| 100 GB | /srv/easydb | fast storage |
| 2000 GB | /srv/easydb/eas/lib/assets | network storage |
Probably only the latter two storage types need to grow, if you add more assets later.
Example “maximum separation”:
| storage space | directory | candidate for … |
|---|---|---|
| 30 GB | / | |
| 1 GB | /boot | |
| 60 GB | /var/lib/docker | fast storage (low priority) |
| 50 GB | /srv/easydb/eas/tmp | fast storage (low priority) |
| 20 GB | /srv/easydb/easydb-server/var | fast storage (low priority) |
| 20 GB | /srv/easydb/elasticsearch/var | fast storage (high priority) |
| 20 GB | /srv/easydb/pgsql/var | fast storage (high priority) |
| 10 GB | /srv/easydb/pgsql/backup | network storage |
| 2000 GB | /srv/easydb/eas/lib/assets | network storage |
Please note that the maximum separation needs more storage and adjustments over time. We therefore advise against it. In the less separated approach, more directories can use more of the storage space. Which directories need how much space depends on your data model and configuration. These both may change and are different from customer to customer. Thus we cannot predict reliable numbers.
Network
The domain name (“URL”) of the easydb should be known during installation, so that it can be configured right away. It can be changed later and more addresses can be added later. One domain name is the primary, however, and is used for image URLs. If you use https at all then the primary domain must also have https.
easydb needs a domain or subdomain of its own. Or an IP address.
For example “https://media.example.com” or “http://1.2.3.4” but not “https://example.com/media”.
The “/media” part of the URL is called “path”. A static path is not supported by easydb, instead it generates a multitude of paths itself dynamically during use.
The easydb also communicates with its users via e-mail.
- An SMTP relay is specified in the easydb configuration.
- Also a sender address domain name, which must be accepted by the relay and by the receiving server (thus the domain usually has to be valid on the whole Internet).
Firewall
Among firewall software, we only know of one that is compatible with docker’s firewall rules: shorewall with at least version 5.2.1.1
Therefore if there has to be a firewall on your easydb host, we only support this one.
Connections during installation
Specifically, if we are installing on one of your servers, the following connections should be allowed.
If these are not possible, we still have at least two alternative approaches: You can install on your server; or we install on our servers (which then needs a hosting contract).
Connections to the server
For installation, maintenance and monitoring we need HTTPS (Port 443) and SSH access to the server.
Our approach is:
SSH is encrypted, secure and state of the art, even as a permanently open port.
- The account has to have administrative rights, either directly as root or via “sudo” or “su”.
- Access can be granted by password or - preferred - by our public ssh key: https://www.programmfabrik.de/files/sshkey4096.txt .
- Optional: The access may be restricted to our IP address. We are using the IP address of bern.programmfabrik.de (and if you can allow more than one, berlin.programmfabrik.de) as source IP address during access.
- Optional: The port can be configured by the customer. The default is 22.
- Optional: The access can be secured via a customer operated SSH proxy (also known as Jumphost).
- Optional: Additionally, a customer operated OpenVPN server can be used or a customer operated Cisco-SSL-VPN server(if it is compatible with “OpenConnect”) can be used.
We recommend that we test SSH access a few working days prior to the installation, whereby we also check the prerequisites of the server.
We will be using the automation software “ansible” for installation, which is built upon SSH. Almost all SSH-connections are suited for ansible, but if in doubt about a certian SSH-jumphost installation, you (or we) can test it by connecting with ansible.
The installation takes several minutes or a few hours in case of complications.
Access via SSH or SSH + OpenVPN
The graphic below compares two supported access paths:
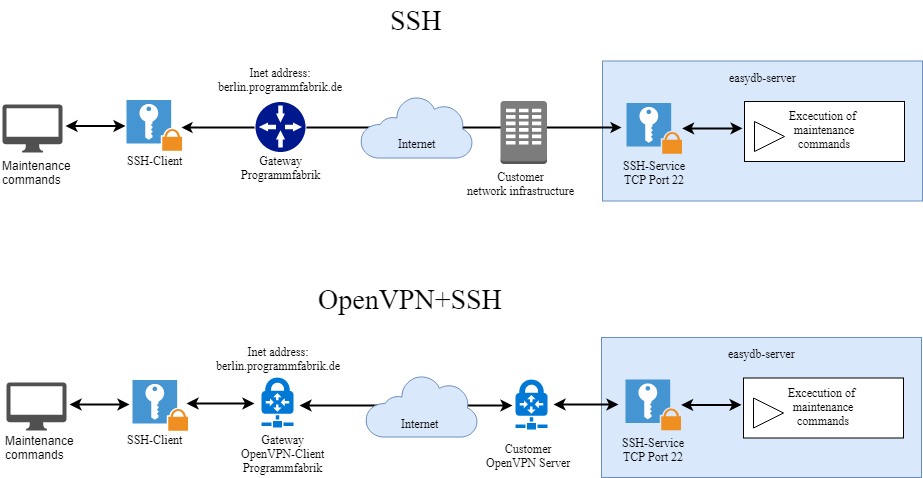
Connections from the server to the Internet
This information applies during installation and normal operation (for updates).
- During the installation docker.easydb.de is being accessed via HTTPS.
- Also package sources of the Linux distribution (Debian or Ubuntu) are accessed via http and package sources of Docker at download.docker.com via https.
- Optional: Use of an HTTP(S) proxy is possible.
Proxy
If you want the easydb host to reach the Internet by a proxy, then configure this proxy for …
-
Container management software
Please refer to your container management documentation. To get you started, here an example for docker with systemd:
In
/lib/systemd/system/docker.serviceor/etc/systemd/system/docker.service.d/proxy.conf:[Service] Environment="http_proxy=http://10.80.80.80:8080/" "https_proxy=http://10.80.80.80:8080/"systemctl daemon-reload systemctl docker.service stop # beware: stops all containers systemctl docker.service start -
Operating System Updates
Please refer to your operating system documentation. To get you started, here an example for Debian:
In
/etc/apt/apt.conf:Acquire::http::Proxy "http://10.80.80.80:8080"; -
Map into container
In some cases it is necessary to map the proxy into the server-, eas- or chrome-container. Add this to your
docker runcommand:--env=HTTP_PROXY=http://proxy.example.com:3128 \ --env=http_proxy=http://proxy.example.com:3128 \ --env=HTTPS_PROXY=https://proxy.example.com:3128 \ --env=https_proxy=https://proxy.example.com:3128 \ --env=NO_PROXY=easydb-pgsql,easydb-elasticsearch,easydb-eas,easydb-server,easydb-fylr,chrome \ --env=no_proxy=easydb-pgsql,easydb-elasticsearch,easydb-eas,easydb-server,easydb-fylr,chrome \
Integration
Further integration into your network is quite possible, but this is not treated as part of the installation. We recommend installation as a first step.
Examples for further integration:
- HTTPS, with your certificate
- LDAP, SSO, Active Directory
- Define an import directory for assets that you can populate by …
- Windows Explorer and other “webdav” clients
- NFS
- SMB / CIFS
Advanced
Concrete steps of installation of easydb 5.